IELTS Reading Test Guide
The International English Language Testing System (IELTS) is a pivotal stepping-stone for those planning to study, live, or work where English is the language of communication. It assesses the test taker’s ability to listen, read, write, and speak in English. This comprehensive guide will focus on the Reading component of the IELTS, offering insight into its format, preparation strategies, and ways to avoid common pitfalls.
Introduction
The IELTS Reading Test is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including the gist, main ideas, details, logical arguments, the opinions of writers, and the purpose of written texts. This test is crucial for college applicants, international students, and even professionals who need to demonstrate their English proficiency.
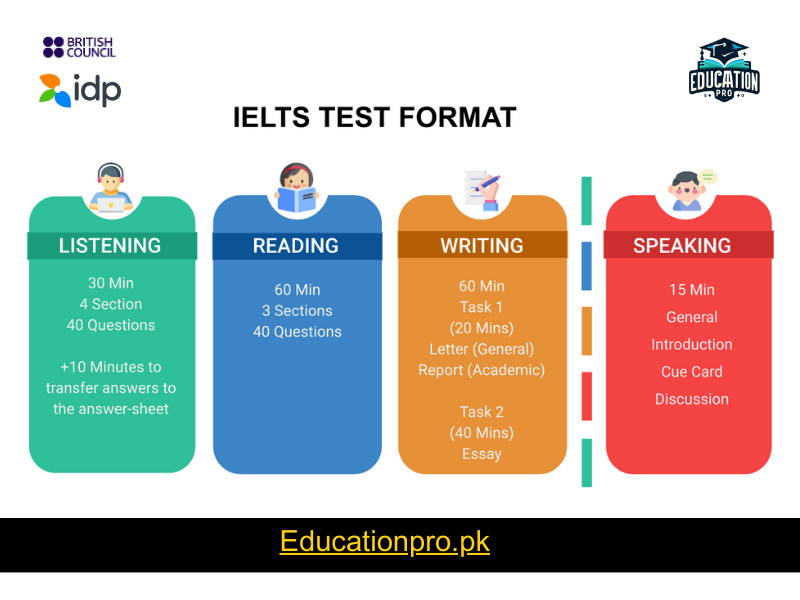
Pattern of IELTS Reading Test
The IELTS has two versions — Academic and General Training. Both include a 60-minute Reading section, but the content differs slightly:
IELTS Academic Reading:
- Time Allowed: 60 minutes
- Number of Passages: 3
- Length: About 2150 to 2750 words across all passages
- Types of Texts: Includes texts from books, journals, newspapers, and magazines intended for an academically-oriented audience.
IELTS General Training Reading:
- Time Allowed: 60 minutes
- Number of Sections: 3
- Length: Around 2000 to 2750 words across all sections
- Types of Texts: Excerpts from books, magazines, newspapers, notices, advertisements, company handbooks, and guidelines. These are materials you are likely to encounter on a daily basis in an English-speaking environment.
Both versions of the test can include diagrams, graphs, or illustrations, and you might be tasked with labeling a diagram or completing a summary.
Detailed Explanation of the IELTS Reading Test Pattern
The IELTS Reading Test, whether you opt for the Academic version or the General Training version, is designed to assess a wide range of reading skills. Understanding the detailed pattern and what each part attempts to evaluate can significantly enhance your preparation strategy.
Academic Reading Test Detailed Pattern
- Content Variety: The Academic Reading Test includes three long passages that range in complexity. The first passage is typically the easiest, with the difficulty level increasing with each subsequent passage. This structure is intended to test your ability to understand main ideas, details, implications, and the writer’s attitude across a variety of subjects.
- Question Types: The test includes around 10-14 questions for each passage, comprising a mix of multiple-choice, identifying information (true/false/not given), matching information/headings/features, sentence completion, summary completion, and note/table/flow-chart completion. This variety evaluates your ability to process information in different forms and under time constraints.
- Text Sources: The texts are sourced from authentic academic materials that reflect the type of reading an undergraduate or postgraduate student might encounter in an English-speaking environment. These sources are chosen for their intellectual challenge and their representation of current academic discourse.
General Training Reading Test Detailed Pattern
- Section Overview: The General Training Reading Test is structured into three sections. Section 1 contains two or three short factual texts, Section 2 comprises two short, work-related, factual texts, and Section 3 features one longer text on a topic of general interest. This progression is designed to test a range of skills from the basic to more developed.
- Real-Life Relevance: The texts in the General Training Test are selected for their relevance to the everyday English environment, such as workplace guidelines, advertisements, and instructional materials. This design choice ensures that the test is practical and reflects the real-world usage of English.
- Skill Assessment: Like the Academic version, the General Training Test evaluates a mix of skills via various question
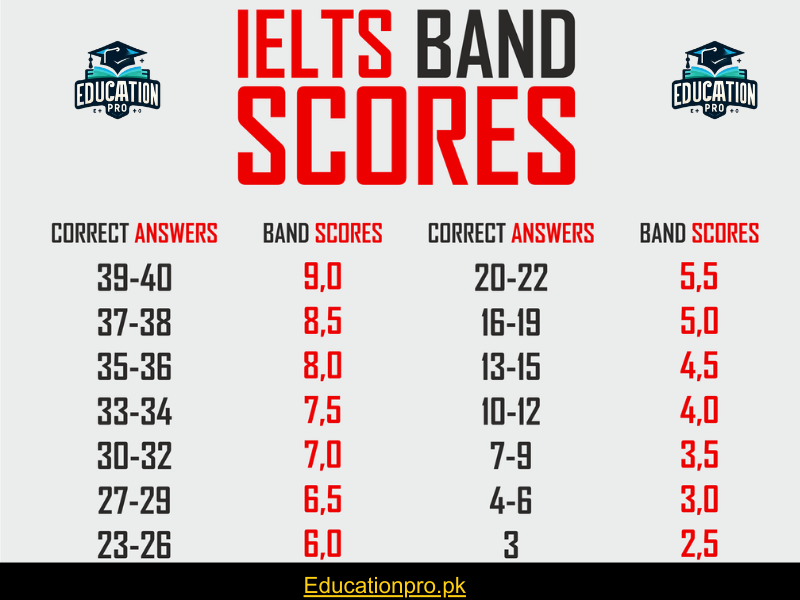
Bands Distribution
The IELTS Reading Test scores are reported in bands ranging from 0 to 9. Each correct answer is awarded one mark, and scores out of 40 are converted to the IELTS nine-band scale. They are presented as whole or half bands for each section of the test. The band score reflects your proficiency level, with band 9 indicating an expert user and band 0 for those who did not attempt the test.
How to Prepare
Preparing for the IELTS Reading Test requires a multifaceted approach:
- Regular Practice: Familiarize yourself with different types of reading materials, including the ones mentioned above. Make reading a daily habit to build speed and comprehension.
- Understand Question Formats: Practicing various types of questions such as multiple-choice, true/false/not given, matching headings, and others will help you become adept at the test format.
- Time Management: Since you have a limited time to answer 40 questions, practice under timed conditions to build your speed.
- Develop Strategies: Learn strategies like skimming and scanning, keyword identification, and paraphrasing to find information quickly and understand the main points without reading every word.
Common Mistakes in IELTS Reading Test
Some of the typical mistakes test-takers make are:
- Mismanagement of Time: Spending too much time on difficult questions can cause you to run out of time for easier ones.
- Careless Errors: Failing to follow instructions, such as writing more words than required, can cost you marks.
- Lack of Practice with Different Types of Questions: Being unfamiliar with the question types can lead to confusion and incorrect answers.
Tips For IELTS Reading Test
- Don’t leave any blanks: Even if you’re unsure, it’s better to guess than to leave an answer blank.
- Look out for paraphrasing: The answers are often paraphrased and may not match the exact wording in the text.
- Move on if stuck: If you can’t find an answer, save time by moving on and return to it later if time permits.
- Practice with full-length tests: This will give you an idea of what to expect and help you feel more comfortable on test day.
- Improve Vocabulary: A wide range of vocabulary will aid in understanding texts and answering questions more accurately.
academic reading , ielts online test reading , ielts general training reading , ielts reading examples , ielts reading , ielts reading practice test , ielts reading practice , ielts reading test , ielts reading mock test , ielts reading exam , ielts exam reading test , ielts reading practise test , ielts general reading practice test , ielts reading materials , reading passage for ielts , ielts academic reading , ielts reading test online , reading test ielts general , Educationpro

FAQs
Q: Is the IELTS Reading Test paper-based or computer-based?
A: It can be both. You can choose the option that suits you best.
Q: Can I use a pen for the IELTS paper-based test?
A: No, you must use a pencil as your answers are scanned by a computer.
Q: How important is spelling in the Reading Test?
A: Spelling is very important. Be careful when transferring your answers to the answer sheet – incorrect spelling will be marked wrong.
Q: Is the Academic IELTS Reading Test harder than the General Training Test?
A: The Academic test contains texts that are more challenging than the General Training test. However, the scoring requirements for obtaining a particular band are usually tougher in the General Training test.
Q: Can I write on my test paper?
A: Yes, you can make notes and mark key pieces of information.
Q: Should I read the passage first or the questions?
A: Strategies vary, but most students find it helpful to quickly skim the questions first and then read the passages in order to know what information to look for.
In conclusion, success in the IELTS Reading Test hinges on understanding the test format, diligent practice, and learning strategies that can help you work efficiently under pressure. With consistent preparation over time and a clear understanding of common errors and how to address them, you can aim for a high band score. Remember to keep improving your language skills, as this will serve you well beyond test day.

